St Pauls, Index
CHAPTER I.
THE BUILDING.
Roman London—The Beginning of Christian London—The English Conquest and London once more Heathen—The Conversion—Bishop Mellitus—King Sebert—The First Cathedral—Its Destruction—Foundation of the Second Cathedral by Bishop Maurice—Another Destructive Fire—Restoration and Architectural Changes—Bishop Fulk Basset's Restoration—The Addition Eastward—St. Gregory's Church on the S.W. side—"The New Work" and a New Spire: dedicated by Bishop Segrave—How the Money was raised—Dimensions of the Old Church—The Tower and Spire—The Rose Window at the East End—Beginning of Desecration.
The Romans began the systematic conquest of Britain about the time of Herod Agrippa, whose death is recorded in Acts xii. London was probably a place of some importance in those days, though there is no mention of it in Cæsar's narrative, written some eighty years previously. Dr. Guest brought forward reasons for supposing that at the conquest the General Aulus Plautius chose London as a good spot on which to fortify himself, and that thus a military station was permanently founded on the site of the present cathedral, as being the highest ground. If so, we may call that the beginning of historic London, and the Romans, being still heathen, would, we may be sure, have a temple dedicated to the gods close by. Old tradition has it that the principal temple was dedicated to Diana, and it is no improbable guess that this deity was popular with the incomers, who found wide and well-stocked hunting grounds all round the neighbourhood. Ages afterwards, in the days of Edward III., were found, in the course of some exhumations, vast quantities of bones of cattle and stags' horns, which were assumed to be the remains of sacrifices to the goddess. So they may have been; we have no means of knowing. An altar to Diana was found[page 2] in 1830 in Foster Lane, close by, which is now in the Guildhall Museum.
But not many years can have passed before Christianity had obtained a footing among the Roman people; we know not how. To use Dr. Martineau's expressive similitude, the Faith was blown over the world silently like thistle-seed, and as silently here and there it fell and took root. We know no more who were its first preachers in Rome than we do who they were in Britain. It was in Rome before St. Paul arrived in the city, for he had already written his Epistle to the Romans; but evidently he made great impression on the Prætorian soldiers. And we may be sure that there were many "of this way" in the camp in London by the end of the first century. For the same reason we may take it for granted that there must have been a place of worship, especially as before the Romans left the country Christianity was established as the religion of the Empire. Only two churches of the Roman period in England can now be traced with certainty. Mr. St. John Hope and his fellow-explorers a few years ago unearthed one at Silchester, and the foundations of another may be seen in the churchyard of Lyminge in Kent.
And this is really all we can say about the Church in London during the Roman occupation. The story of King Lucius and that of the church of St. Peter in Cornhill are pure myths, without any sort of historical foundation, and so may be dismissed without more words.
The Romans went away in the beginning of the fifth century, and by the end of the same century the English conquest had been almost entirely accomplished. For awhile the new comers remained heathens; then came Augustine and his brother monks, and began the conversion of the English people to Christ. The king of Kent was baptized in 596, and Canterbury became the mother church. Pope Gregory the Great sent Augustine a reinforcement of monks in 601. Two of these, Laurentius and Mellitus, were consecrated by Augustine as missionary bishops to convert West Kent and the East Saxon Kingdom to the faith. The chief town of the former district was Rochester, and of the latter London. This city had much grown in importance, having established a busy trade with the neighbouring states both by land and sea. The king of the East Saxons was Sebert, nephew of Ethelbert of Kent, and subject to him. He, therefore, received Mellitus with cordiality,[page 3] and as soon as he established his work in the city, King Ethelbert built him a church wherein to hold his episcopal see, and, so it is said, endowed it with the manor of Tillingham, which is still the property of the Dean and Chapter of St. Paul's. There is no portion of that old church remaining. It was in all probability built mostly of wood, and it perished by fire, as so many Anglo-Saxon churches did, on July 7th, 1087. Some historical incidents connected with that early building will be found on a subsequent page.
In the year before this calamity (April 5th, 1086), Maurice, chaplain and chancellor to William the Conqueror, had been consecrated Bishop of London by Lanfranc. Unlike most of William's nominees to bishoprics, Maurice's moral character was disreputable; but he was a man of energy, and he set to work at once to rebuild his cathedral, and succeeded in getting from the king abundance of stone for the purpose, some of it from the remains of the Palatine tower by the side of the Fleet River, which was just being pulled down, having been hopelessly damaged by the fire,1 and some direct from Caen. William also at the same time gave him the manor and castle of Bishop Stortford, thus making him a baronial noble. There was need for haste, for the Conqueror died at Rouen on the 9th of September that same year.
So began the great Cathedral of St. Paul, the finest in England in its time, which, witnessing heavy calamities, brilliant successes, scenes both glorious and sad, changes—some improvements and others debasements—lasted on for nearly six centuries, and then was destroyed in the Great Fire. We have first to note the main features of the architectural history.
Bishop Maurice began in the Norman style, as did all the cathedral-builders of that age, and splendid examples of their work are still to be seen in our cities. Bishop Maurice's, as I have said, was the finest of them all in its inception, but he really did little more than design it and lay the foundations, though he lived until 1108. He seems to have been too fond of his money. His successor, Richard Belmeis, exerted himself very heartily at the beginning of his episcopate, spent large sums on the cathedral, and cleared away an area of mean[page 4] buildings in the churchyard, around which his predecessor had built a wall. In this work King Henry I. assisted him generously; gave him stone, and commanded that all material brought up the River Fleet for the cathedral should be free from toll; gave him moreover all the fish caught within the cathedral neighbourhood, and a tithe of all the venison taken in the County of Essex. These last boons may have arisen from the economical and abstemious life which the bishop lived, in order to devote his income to the cathedral building.
Belmeis also gave a site for St. Paul's School; but though he, like his predecessor, occupied the see for twenty years, he did not see the completion of the cathedral. He seems to have been embittered because he failed in attaining what his soul longed for—the removal of the Primatial chair from Canterbury to London. Anselm, not unreasonably, pronounced the attempt an audacious act of usurpation. Belmeis's health broke down. He was attacked with creeping paralysis, and sadly withdrew himself from active work, devoting himself to the foundation of the monastery of St. Osyth, in Essex. There, after lingering four years, he died, and there he lies buried.
King Henry I. died nearly at the same time, and as there was a contest for the throne ensuing on his death, so was there for the bishopric of London. In the interval, Henry de Blois, the famous Bishop of Winchester, was appointed to administer the affairs of St. Paul's, and almost immediately he had to deal with a calamity. Another great fire broke out at London Bridge in 1135, and did damage more or less all the way to St. Clement Danes. Matthew Paris speaks of St. Paul's as having been destroyed. This was certainly not the case, but serious injury was done, and the progress of the building was greatly delayed. Bishop Henry called on his people of Winchester to help in the rebuilding, putting forward the plea that though St. Paul was the great Apostle of the West, and had planted so many churches, this was the only cathedral dedicated to him. During these years Architecture was ever on the change, and, as was always the custom, the builders in any given case did not trouble themselves to follow the style in which a work had been begun, but went on with whatever was in use then.
Consequently the heavy Norman passed into Transitional, and Early English. For heavy columns clustered pillars were substituted, and [page 5] lancets for round arches. Nevertheless, apparently, Norman columns which remained firm were left alone, while pointed arches were placed over them in the triforium. Even in the Early English clustered pillars there were differences marking different dates, some of the time of the Transition (1222), and some thirty years later. And here let us note that the "Gothic" church, as it is shown in our illustrations, does not indicate that the Norman work had been replaced by it. The clustered pillars really encased the Norman, as they have done in other cathedrals similarly treated. At Winchester, William of Wykeham cut the massive Norman into Perpendicular order, but at St. Paul's an outer encasement covered the Norman, as Wren showed when he wrote his account of the ruined church. A steeple was erected in 1221. There was a great ceremony at the rededication, by Bishop Roger Niger, in 1240, the Archbishop of Canterbury and six other bishops assisting.
In 1255 it became necessary for the Bishop of London (Fulk Basset) to put forth appeals for the repair of the cathedral, and his ground of appeal was that the church had in time past been so shattered by tempests that the roof was dangerous. Some notes about these tempests will be found in a subsequent page. Accordingly this part was renewed, and at the same time the cathedral church was lengthened out eastward. There had been a parish church of St. Faith at the east end, which was now brought within the cathedral. The parishioners were not well content with this, so the east end of the crypt was allotted to them as their parish church, and they were also allowed to keep a detached tower with a peal of bells east of the church. This tower had already an historic interest, for it had pealed forth the summons to the Folkmote in early days, when that was held at the top of Cheapside. This eastward addition was known all through the after years as "The New Work." It is remarkable to note how much assistance came from outside. Hortatory letters were sent from the Archbishops of Canterbury and York, as well as from the greater number of other bishops, to their respective dioceses. And not only so, but eight Irish dioceses and one Scotch (Brechin) also sent aid.
There was another parish church hard by, that of St. Gregory-by-St. Paul. Almost all our cathedrals have churches close to them, such as St. Margaret's, Westminster; St. Laurence, Winchester; St. John's,[page 6] Peterborough; St. Nicholas, Rochester. In all cases they are churches of the parishioners, as contrasted with those of the monastery or the cathedral body. St. Gregory's Church was not only near St. Paul's, but joined it; its north wall was part of the south wall of the cathedral. Its early history is lost in antiquity, but it was in existence before the Conquest.2 The body of St. Edmund, K. & M., had been preserved in it during the Danish invasions, before it was carried to Bury St. Edmunds by Cnut for burial. It shared the decay of the cathedral, and in the last days it was repaired, as was the west end, by Inigo Jones in his own style, as will be seen by the illustrations. Of the tombs and chantries which had by this time been set up, it will be more convenient to speak hereafter, as also of the deanery, which Dean Ralph de Diceto (d. 1283) built on its present site.
Before the end of the thirteenth century Old St. Paul's was complete. In the first quarter of the fourteenth century, a handsome marble pavement, "which cost 5d. a foot," was laid down over "the New Work," eastward, and the spire, which, being of lead over timber, was in a dangerous condition, was taken down and a very fine one set in its place, surmounted by a cross and a gilt pommel3 large enough to contain ten bushels of corn. Bishop Gilbert Segrave (who had previously been precentor of the cathedral, and was bishop from 1313 to 1317) came to the dedication. "There was a great and solemn procession and relics of saints were placed within" (Dugdale). But the following extract from a chronicle in the Lambeth library is worth quoting: "On the tenth of the calends of June, 1314, Gilbert, Bishop of London, dedicated altars, namely, those of the Blessed Virgin Mary, of St. Thomas the Martyr, and of the Blessed Dunstan, in the new buildings of the Church of St. Paul, London. In the same year the cross and the ball, with great part of the campanile, of the Church of St. Paul were taken down because they were decayed and dangerous, and a new cross, with a ball well gilt, was erected; and many relics of divers saints were for the protection of the aforesaid campanile[page 7] and of the whole structure beneath, placed within the cross, with a great procession, and with due solemnity, by Gilbert the bishop, on the fourth of the nones of October; in order that the Omnipotent God and the glorious merits of His saints, whose relics are contained within the cross, might deign to protect it from all danger of storms. Of whose pity twenty-seven years and one hundred and fifty days of indulgence, at any time of the year, are granted to those who assist in completing the fabric of the aforesaid church."
[plate 2]

A
BISHOP
PLACING
RELICS IN AN
ALTAR.
From a Pontifical of the Fourteenth Century. British Museum, Lans.
451.
[plate 3]

A
PAPAL
LEGATE.
From the Decretals of Boniface VIII. British Museum, 23923.
In the Bodleian Library there is an inventory of these relics, amongst them part of the wood of the cross, a stone of the Holy Sepulchre, a stone from the spot of the Ascension, and some bones of the eleven thousand virgins of Cologne.
The high altar was renewed in 1309 under an indented covenant between Bishop Baldock and a citizen named Richard Pickerill. "A beautiful tablet was set thereon, variously adorned with many precious stones and enamelled work; as also with divers images of metal; which tablet stood betwixt two columns, within a frame of wood to cover it, richly set out with curious pictures, the charge whereof amounted to two hundred marks."
Dugdale also tells of "a picture of St. Paul, richly painted, and placed in a beautiful tabernacle of wood on the right hand of the high altar in anno 1398, the price of its workmanship amounting to 12l. 16s.."
Quoting from a MS. of Matthew of Westminster, he gives the dimensions of the church, in the course of which he says the length was 690 feet. This is undoubtedly wrong, as Wren showed. I take the measurements from Mr. Gilbertson's admirable little handbook, who, with some modifications, has taken them from Longman's Three Cathedrals.
| Breadth | 104 ft. |
| Height of Nave roof to ridge of vaulting | 93 ft. |
| " Choir | 101 ft. 3 in. |
| " Lady Chapel | 98 ft. 6 in. |
| " Tower from the ground | 285 ft. |
| " Spire from parapet of tower | 204 ft. |
| " Spire from the ground | 489 ft. |
| Length of church (excluding Inigo Jones's porch) | 586 ft. |
Wren (Parentalia) thinks this estimate of the spire height too great;[page 8] he reckons it at 460 feet.
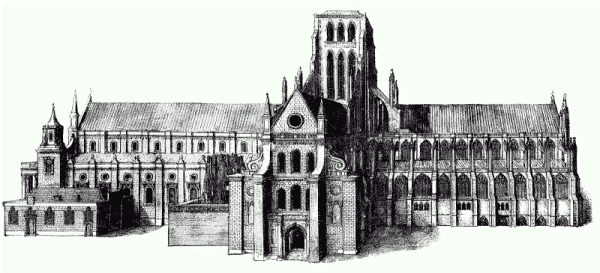
The cathedral resembled in general outline that of Salisbury, but it was a hundred feet longer, and the spire was sixty or eighty feet higher. The tower was open internally as far as the base of the spire, and was probably more beautiful both inside and out than that of any other English cathedral. The spire was a structure of timber covered with lead. In Mr. Longman's Three Cathedrals are some beautiful engravings after a series of drawings by Mr. E.B. Ferrey, reproducing the old building. There is one curious mistake: he has not given at the base of the spire, the corner pinnacles on the tower, which were certainly there. They are clearly shown in Wyngaerde's drawing of London, and on a seal of the Chapter, which we reproduce. Some time later than the rest of the work, stately flying buttresses were added to strengthen the tower walls. One special feature of the cathedral was the exquisite Rose window at the east end, of which we give an engraving. It had not a rival in England, perhaps one might say in Europe. Inigo Jones, if he was really the architect of St. Katharine Cree, made a poor copy of it for that church, where it may still be seen.
Of great historical events which had occurred during the growth of St. Paul's cathedral we have to speak hereafter. As the momentous changes of the sixteenth century drew near, the godlessness and unbelief which did so much to alienate many from the Church found strong illustrations in the worldliness which seemed to settle down awhile on St. Paul's and its services. Clergymen appeared here to be hired (Chaucer's Prologue), and lawyers met their clients. Falstaff "bought Bardolph at Paul's." But before we come to the great changes, it will be well to go back and take note of the surroundings of the cathedral, and also to stroll through the interior, seeing that we have now come to its completion as a building, except for one addition, a real but incongruous one, which belongs to the Stuart period. The accession of Henry VIII. then sees it, with that exception, finished, and we discern three main architectural features: there is still some heavy Norman work, some very excellent Early English, and some late Decorated. And there are also tombs of deep interest; though they are not to be compared indeed with those of Westminster Abbey. There are only two Kings to whom we shall come in our walk. But let us have the outside first.
[plate 4]
OLD ST. PAUL'S, FROM THE SOUTH. After W. Hollar.
[plate 5]
OLD ST. PAUL'S, FROM THE NORTH. After W. Hollar.
[plate 6]
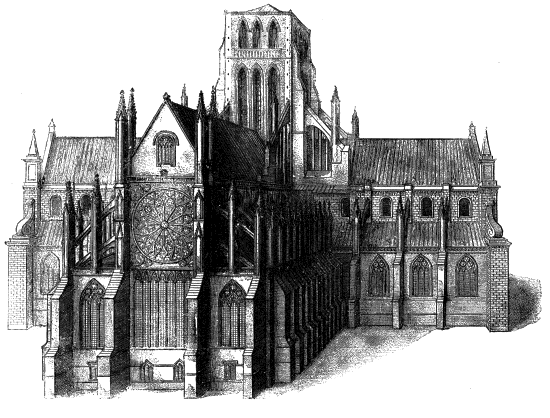
OLD ST. PAUL'S, FROM THE EAST. After W. Hollar.
[plate 7]
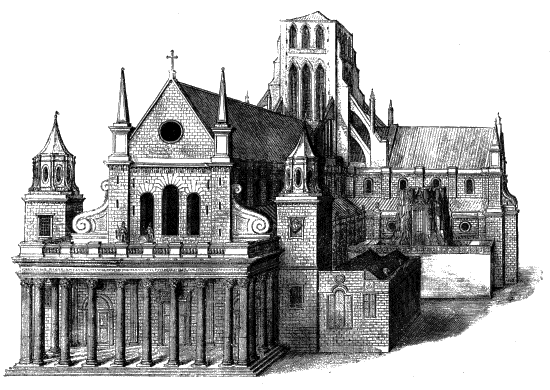
OLD ST. PAUL'S, FROM THE WEST. After W. Hollar.
[page 9]
And Last updated on: Thursday, 09-Jan-2025 14:15:35 GMT